|
What are electric cars and how do they work?
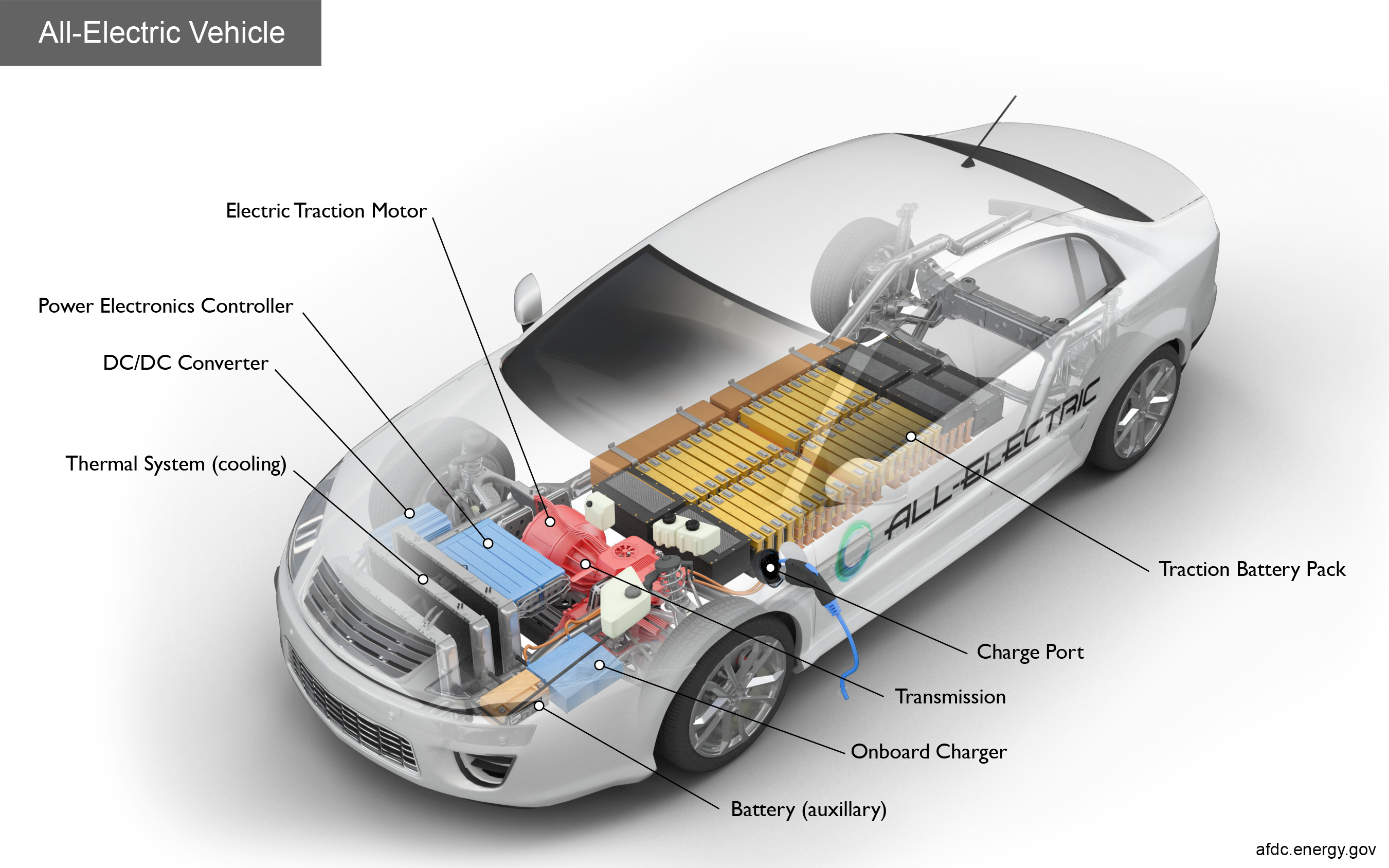
Electric cars are a type of vehicle that have onboard rechargeable battery packs.
They can be plugged into the electric grid and charged from there. In addition, the electricity stored
inside of the vehicle is the only energy source that provides propulsion for the wheels. Electric motors
have the ability to provide high power-to-weight ratios, and it is possible for batteries to be designed
with the purpose of supplying the electrical current and in turn, supporting the motors. Electric motors
have a flat torque curve down to zero speed, meaning it can produce the most torque at the “lower to
middle end” of its speed. This helps acceleration and doesn’t cause as many gear shifts while driving.
Finally, most electric cars have no clutch and use fixed-ratio gearboxes - this design is simple and
reliable.
|
click here
 |
|
What are the pros and cons of electric cars?
Pros: Electric cars are much more energy efficient than traditional gasoline
powered vehicles. Electric batteries can convert anywhere between 59 - 62 percent of energy into vehicle
movement, whereas gas powered vehicles are capable of transferring merely 17-21 percent of energy into
vehicle movement. Also, electric cars reduce emissions. Since they rely on rechargeable batteries,
electric cars don’t pollute the environment in any way. Finally, electric cars have higher performance,
lower maintenance, and can be recharged at home.
Cons: On average, electric cars have a shorter driving range than gasoline powered cars. Most models range between 60 and 120 miles per charge, and some luxury models can reach a range of 300 miles per charge
(the same as an average gas-powered vehicle). In addition, electric cars take longer to recharge. Fully recharging the vehicle can take up to 8 hours, and even fast charging stations need 30 minutes to charge a vehicle to
80 percent capacity. Finally, electric cars are more expensive, and the battery packs may need to be replaced multiple times throughout the lifetime of the car.
|
click here
 |
|
History of electric cars
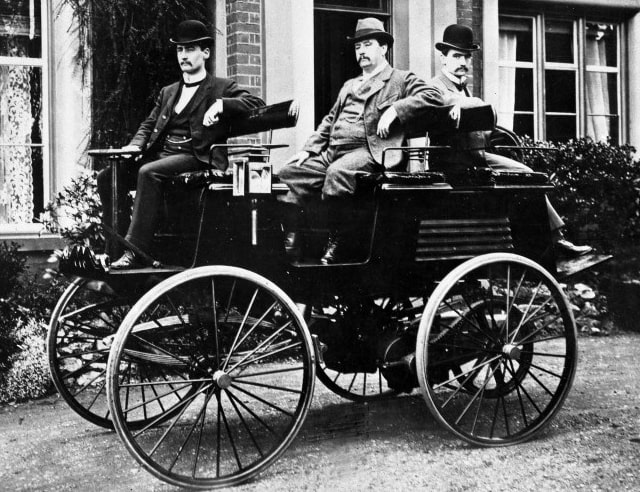
The first successful electric car was made in the U.S. by William Morrison in
1890. Electric cars became more common in the 1910s, as it became easier to charge them. However, Henry
Ford's Model T was more affordable, so electric cars didn't sell as much. By 1935, electric cars had all
but disappeared. 30 years later, in the late 1960s and early 1970s, gas got more expensive, but despite
that, electric cars were still less versatile than gas powered cars. In the 1990s, automakers started
making some of their popular vehicle models into electric vehicles, but due to high production costs,
they were discontinued. In 2000, the Tyota Prius was introduced worldwide, and was an instant success.
click here
|
 |


